Relative frequency bar graph
Another name for the vertical bar charts is the column charts. The y-axis of the bars shows the frequencies or relative frequencies and the x-axis shows the values.

Chapter 2
Tables may also present the cumulative relative frequency of the variable.

. In the same histogram the number count or multiple occurrences in the data for each column is represented by the y-axis. A Rectangle Placed Relative to the Axis Position and Length. How to Do a Survey.
Each data category is displayed in a frequency distribution pattern. For example the first cumulative frequency is simply equal to the first frequency of 20. A bar graph shows comparisons among discrete categoriesOne axis of the chart shows the specific.
In the following example the TABLES statement is used to create both a 1-way frequency table for the Origin variable and a 3x3 frequency table for the DriveTrain variable crossed with Origin. A relative frequency histogram is a kind of graphical representation only. The second cumulative frequency is the sum of the first two frequencies.
Bar graphs measure the frequency of categorical data. A bar graph is a chart that plots data with rectangular bars representing the total amount of data for that category. A relative frequency is a frequency divided by the count of all values.
Frequency Distribution and Grouped Frequency Distribution. A frequency or absolute frequency is the count of a value occurrences within a data set. On the other hand the cumulative frequency distribution provides subtotals of all the previous frequencies in the frequency distribution.
We have learned that a line graph is a graph with a line connecting the. 20 21 41. A bar graph is a pictorial rendition of statistical data in which the independent variable can attain only certain discrete values.
A bar chart or bar graph is a chart or graph that presents categorical data with rectangular bars with heights or lengths proportional to the values that they represent. Show each data category in a frequency distribution. It uses either the number of individuals in each group also called the frequency or the percentage in each group called the relative frequency.
This type of graph is used with quantitative data. The height of the bars is according to the relative frequency of the numbers of data given in the element. A relative frequency is the proportion or fraction of times a value occurs in a data set.
Stem and Leaf Plots. Think of how we construct and form sentences in English by combining different elements like nouns verbs articles subjects. Allows for visualization of relative numbers or proportions of.
There are different types of frequencies. What are the Types of Bar Graph. In statistics a frequency distribution is a list table or graph that displays the frequency of various outcomes values in a data set.
An Experiment with a Die. The app provides you a few popular ternary plot templates to show the relative compositions of soils. In this case it was found that 506 of study subjects.
Rotation stretching or skewing. How to Calculate Percent Increase with Relative Cumulative Frequency Tables 547. Reading Interpreting Bar Graphs.
The third cumulative frequency is the sum of the first three frequencies. Within Proc Freq you have the ability to create either dot or bar plots which can be created based on either the frequencies or the overall percentages. Min max mean median or percent frequency.
Each value is represented by a bar and the length or height of the bar shows the frequency of the value. Frequency distribution is a representation either in a graphical or tabular format that displays the number of observations within a given interval. Basic bar graph with connected line to show the trends.
This visualization from Dashflows uses a Pareto chart to display the relative frequency of reasons for non-delivery Using a Pareto chart format allows for a clear comparison. 21 The grammar of graphics. The frequency refers to the number of times a particular value or range of values called a class appears in a data set and relative frequency refers to the percentage of the total data which.
Vertical bar graph horizontal bar graph stacked bar graph and grouped bar graph. A histogram often looks similar to a bar graph but they are different because of the level of measurement of the data. The dependent variable may be discrete or continuous.
How to use relative frequency. Continuous Data can take any value within a range Examples. There are four types of bar graphs.
Ranges of values called classes are listed at the bottom and the classes with greater frequencies have taller bars. A bar chart is a graph that shows the frequency or relative frequency distribution of a categorical variable nominal or ordinal. The relative frequency or empirical probability of an event is the absolute frequency normalized by the total number of events.
The height of the bar graph that is shaded in represents different amounts. Display relative numbers or proportions of multiple categories. A bar chart is a style of bar graph.
It is a representation of a range of outcomes into columns formation along the x-axis. We start with a discussion of a theoretical framework for data visualization known as the grammar of graphics This framework serves as the foundation for the ggplot2 package which well use extensively in this chapter. As for categorical variables frequency distributions may be presented in a table or a graph including bar charts and pie or sector charts.
The following code places a rectangle that starts at 60 and ends at 70 along the x-axis starting from the left and starts at 80 and ends at 90 along the y-axis. Cumulative Tables and Graphs. A bar chart or bar graph is a chart with rectangular bars with lengths proportional to the values that they represent.
The bars can be plotted vertically or horizontally. Some transforms can be done in real time eg. A vertical bar chart is sometimes called a column chart.
A bar graph or bar chart is perhaps the most common statistical data display used by the mediaA bar graph breaks categorical data down by group and represents these amounts by using bars of different lengths. It is often used to represent. A Pareto graph or chart is a type of bar graph that also features a line graph.
The first known use of bar graphs was in 1917. In some shaped bar graph displays each layer of the graph will lose proportionality in representing amounts but labels can overcome this potential shortcoming. Relative frequency can be used to simplify very large values.
Graph Paper Maker. A bar chart bar graph is a way of showing frequency distribution that represents the data using rectangular bars with heights or lengths corresponding to their values. The intervals must be mutually exclusive and.
Origin supports free transforms of 3D plots. A shape can be placed relative to an axiss position on the plot by adding the string domain to the axis reference in the xref or yref attributes for shapes. With 8 years of education which corresponds to 205 of the subjects.
Summarize a large amount of data in a. It represents the grouped data vertically. Could be any value within the range of human heights not just certain fixed heights.
A histogram graph is a bar graph representation of data. Mathematical Approach to Find Relative Frequency. The bars are drawn horizontally or vertically.
20 21 13 54.

Histogram How Do You Use Hist To Plot Relative Frequencies In R Stack Overflow

A Complete Guide To Stacked Bar Charts Tutorial By Chartio
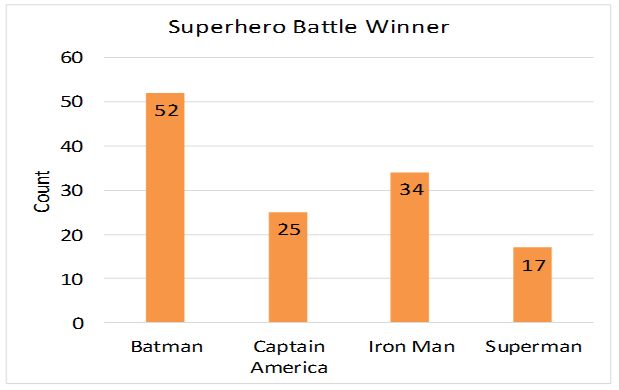
Frequency Tables Pie Charts And Bar Charts

Chapter 2

How To Make A Relative Frequency Histogram In Excel 3 Examples

3 Visualizing Quantitative Data

How To Create A Relative Frequency Histogram In Matplotlib Statology
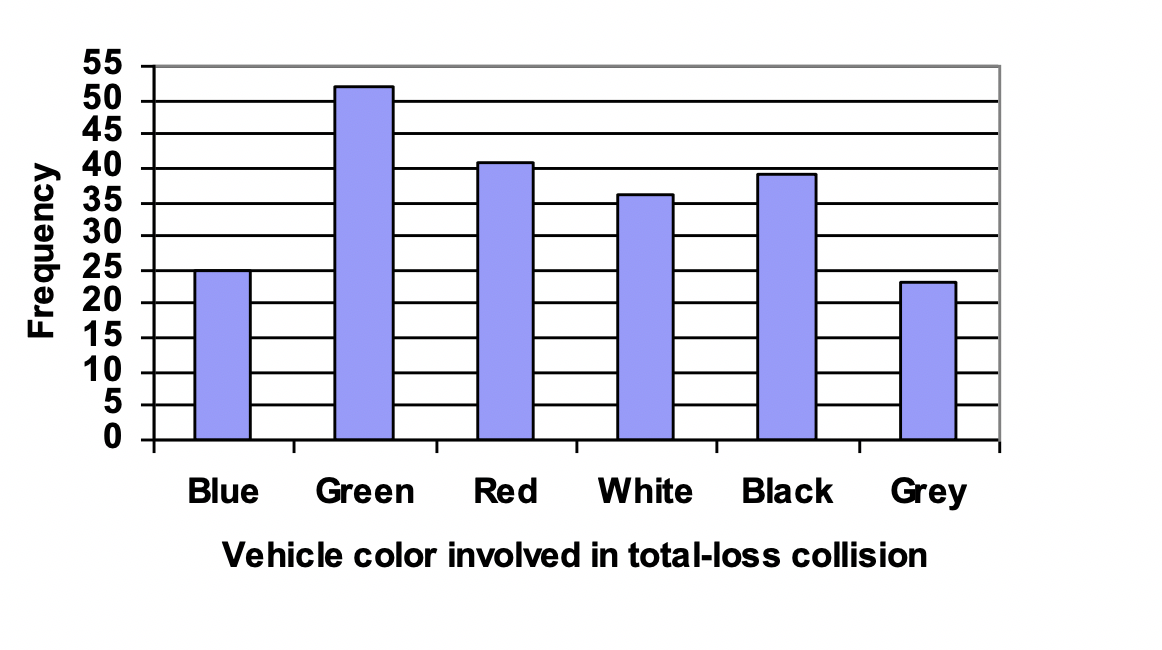
Cm Frequency Tables And Bar Graphs

Relative Frequency Bar Chart Of Settlement Classification Per Cluster Download Scientific Diagram
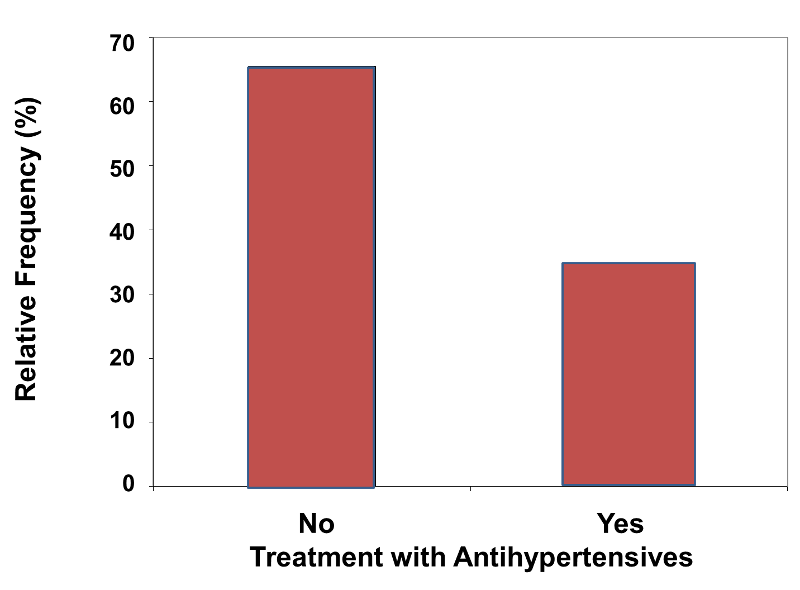
Graphical Summaries For Discrete Variables
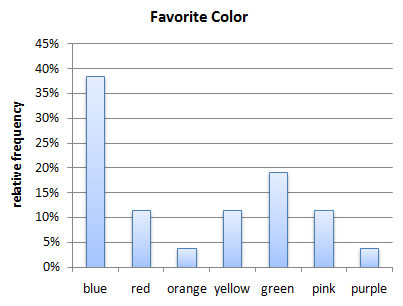
Chapter 2

How To Create A Relative Frequency Histogram In R Statology
Graphs And Charts

Histograms And Frequency Distributions Ck 12 Foundation
Graphs And Charts

Relative Frequencies And Their Distributions Statistics By Jim
Cm Frequency Tables And Bar Graphs